Systems thinking has become a buzzword over the past few years, particularly in relation to climate and sustainability issues. There is, at least, a surface-level consensus that everything is interconnected, and changes in one area can impact others. Some frequently cited examples vividly illustrate the strength of this argument for systems thinking, such as the delay in paddy cultivation to align with the monsoon season (Preservation of Subsoil Water Act 2010), which led to increased wheat stubble burning in the rabi season.

Yet, despite this widespread recognition and appeal, much of the work continues to be carried out in silos with limited integration across sectors, scales, and actors. There is no reconciliation of priorities among different actors.
For instance, our findings indicate that if India’s ethanol blending mandate were to increase beyond E20 (or even maintain E20 through 2030 and beyond), maize cultivation area would need to expand by nearly 4 million hectares to meet all demands, including food and livestock feed. While ethanol blending offers benefits such as reduced crude oil imports, short-term support for farmers’ incomes, and modest reductions in transport sector emissions, it conflicts with the Agriculture Ministry’s priorities for pulse and oilseed self-sufficiency, as well as longer-term foodgrain security. What began as a promising solution to sugar surplus issues risks adversely affecting food security, groundwater resources, land-use changes, and farmer livelihoods in multiple ways. Depending on maize might lock us into a maize intensification system, just like the rice–wheat system that we are now trying to escape.
Similarly, our modelling of India’s land-use dynamics up to 2070 to assess the feasibility of a net-zero scenario revealed critical misalignments. Complete electrification of end-use sectors powered by renewable energy, which is the most commonly modelled net-zero scenario in global integrated assessment models (pushing solar capacity in India to more than 5000 GW, for instance), conflicts with other priorities or goals such as food security, conservation of wastelands or open natural ecosystems, and afforestation and biodiversity conservation. Simply put, there is not enough land to satisfy all these priorities simultaneously (read our report for more details).
There are, of course, several examples of such systems-level analyses at different geographic levels and scales. However, there is usually no ‘designated actor’ responsible for promptly taking up the findings and ‘implementing’ them. Does that mean such studies are too academic with no real-world relevance?
Unfortunately, this seems to be the popular opinion today, particularly in the funding ecosystem. The causal loop diagram below shows how the visible impact of local- or sector-level solutions with immediate actors and beneficiaries/impact reinforces funding for these solutions (R1). This results in reduced priority for systems-level long-term strategy work, which attempts to shift trajectories away from status quo or business-as-usual but often produces outputs with no obvious/direct beneficiaries or responsible actors. Such studies also help identify and prevent lock-ins of infrastructure or policies that seem cost-effective (or ‘cost-optimal’) today but create costly path dependencies in the future. Absence of such work may lead to increased unintended consequences (root causes of sector-specific or localised problems) where no single actor is responsible, yet everyone is affected (R2). The tendency to focus on hyperlocal or siloed problems with the potential for direct and measurable impact is understandable. However, in a world where everything is connected to everything, this may be too narrow-sighted.
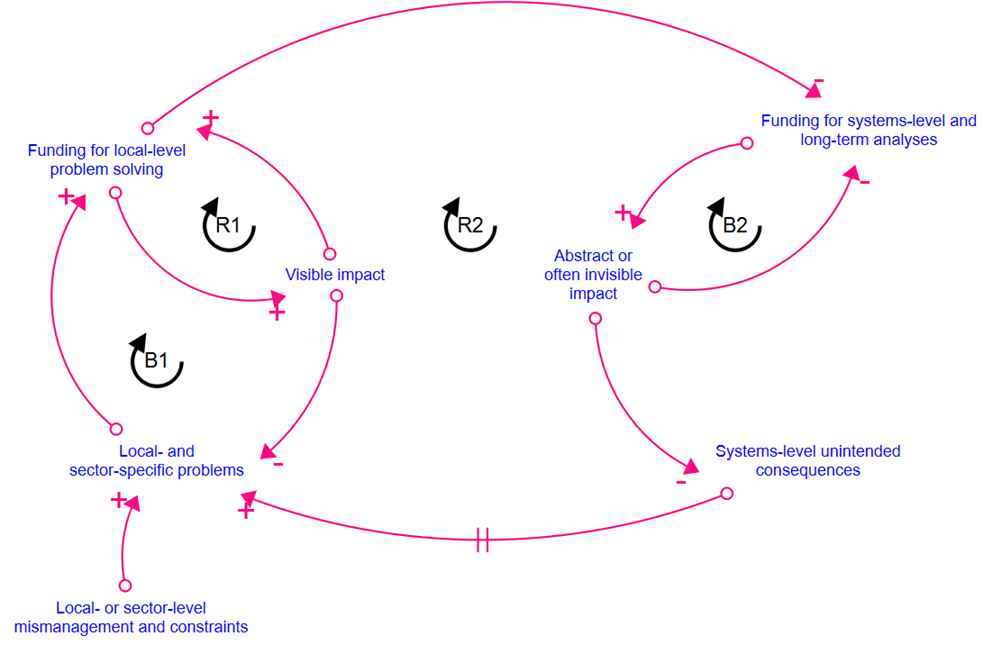
Under conventional impact measurement, systems-level work will go under the radar. For instance, how do you measure the impact of an avoided trade-off that you never anticipated? Yet, such work is essential for climate action and sustainability to move beyond quick fixes and for the economy to undergo structural transformation. When funders question ‘who will use this’ without opportunities to invest in the necessary efforts to sensitise actors to systemic blind spots, the underlying cracks that cause unintended consequences can persist or worsen. Although these studies may not produce immediately visible ‘wins’ that fit into the current impact framework, they will serve as the scaffolding upon which structural transformation can occur by enabling a shared understanding of the system.
Drawing from Donella Meadows’ influential work, the most powerful leverage points—those that can structurally transform systems—are often counterintuitive and resist change, and the system itself pushes back against them. And yet, this challenging work, which involves mapping feedback and revealing unintended consequences, is what can yield a lasting impact. Our research agenda should aim to leverage these long-term levers for unlocking systemic climate transition.
All this is not to suggest that local, sectoral, and visible-impact work should not be prioritised. Rather, it is a plea to prevent systems-level research from being excluded from research agendas.
Funders are uniquely positioned to enable research organisations to generate evidence for mapping the system and sensitising the actors. Only by simultaneously engaging with systemic and local/sector-specific levels can credible evidence be created, allowing implementers and policymakers to identify systemic blind spots and act in coherence. With a funder ecosystem that recognises the potential of building a shared vision, the work on systems-level analyses and local/sector-specific solutions can not only co-exist but also reinforce each other to sustainably drive climate action.
To end with a somewhat arguable metaphor, climate research needs superheroes like both Batman and Superman—Batman, who works quietly preventing disasters behind the scenes, and Superman, who tackles flashy, high-impact rescues. Both approaches are essential, and they must coexist without competing with each other—something even Zach Snyder might now agree with, given how the movie Batman v Superman did!
Ramya Natarajan heads the Climate Change Mitigation team, while Kaveri Ashok heads the Sustainability team at the Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP), a research-based think tank.
More About Publication |
|
|---|---|
| Date | 8 October 2025 |
| Contributors | |
| Publisher | CSTEP |
| Related Areas | |
Get in touch with us at
cpe@cstep.in