Fossil fuels are deeply tied to electricity generation, industrial operations, and transportation among other crucial sectors and cannot be easily dissociated from energy use. CSTEP focuses on a greater integration of renewables and reduction of waste energy in such sectors. This includes working with utilities to improve rooftop solar penetration, mapping potential of various renewables across the country, and analysing energy usage of MSMEs to reduce their fossil fuel consumption.





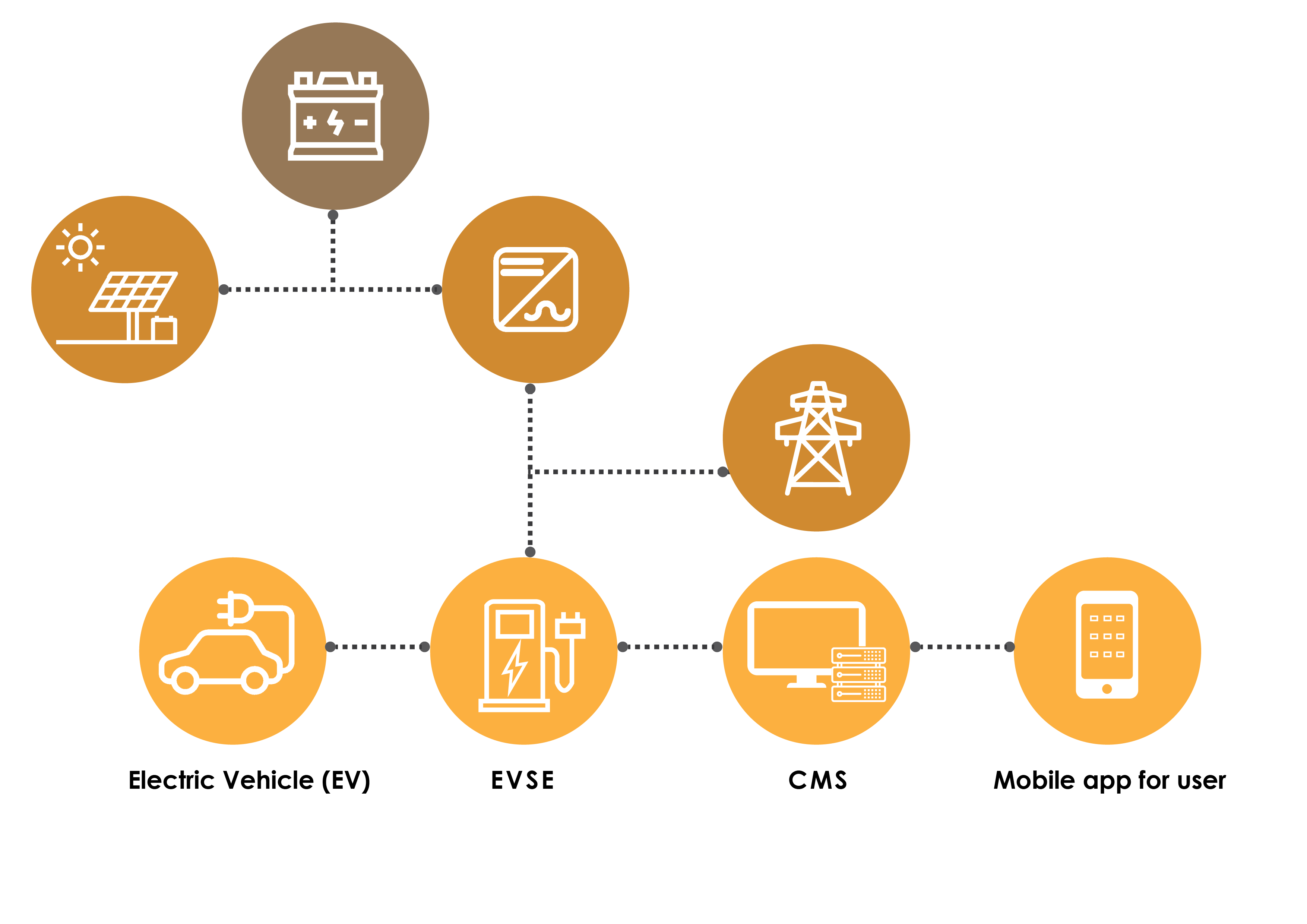
Solar Energy–Based EV Charging: A Pilot Study
CSTEP’s pilot study in collaboration with the state-run Bangalore Electricity Supply Company Limited (BESCOM) demonstrates the idea of directly using solar energy to charge EVs. The project was funded by the Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation.
Sowing the seeds of change for enhanced agricultural credit
The ongoing deliberations around the newly introduced farm laws have redrawn the nation’s focus on farmer-centric issues. Following suit, Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a slew of pro-agrarian measures in the Union Budget, including an agri-credit enhancement to the tune of INR 16.5 lakh crore — highest till date. This move is expected to spur better inputs and cutting-edge technology, making farming less labour-intensive.
Green bonding for recovery
The 2021 Union Budget announced an institutional framework to instill liquidity into the corporate bond market. In sync with the pro-investor move, the country has an opportunity to scale up the green bond market, presently just under one per cent of the total domestic debt market. Green bonds are debt financing instruments for projects that involve renewable energy and energy efficiency, low-carbon infrastructure, and sustainable resource use.
Technology Options and Policy Solutions for a Future Powered by Renewable Energy
Flexibility in the grid is paramount for India to meet its renewable energy (RE) ambitions — 450 GW by 2050 as announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2019. Energy storage systems can enable this flexibility.
Energy storage systems are the next step in India's transition to an RE-dominant future. Although high carbon-emitting thermal energy sources such as coal and petroleum make up a majority of India's energy production, India has set ambitious RE goals — aiming to make RE 80% of its energy mix. Achieving these goals can help India cut its carbon emissions significantly.
How to make rooftop solar attractive to DISCOMs?
India has deployed roughly 300 MW of rooftop solar (RTS) capacity in the first quarter of 2020, taking the overall RTS capacity to 5.74 GW. Yet, the installed capacity falls abysmally short (14%) of the ambitious RTS target of 40 GW by 2022. To make matters worse, the COVID-19 pandemic and the ensuing lockdown brought the RTS sector to a halt — creating a lot of uncertainty. Thus, a strategic and robust plan is essential to revive this segment, as the nation returns to normalcy.