Fossil fuels are deeply tied to electricity generation, industrial operations, and transportation among other crucial sectors and cannot be easily dissociated from energy use. CSTEP focuses on a greater integration of renewables and reduction of waste energy in such sectors. This includes working with utilities to improve rooftop solar penetration, mapping potential of various renewables across the country, and analysing energy usage of MSMEs to reduce their fossil fuel consumption.
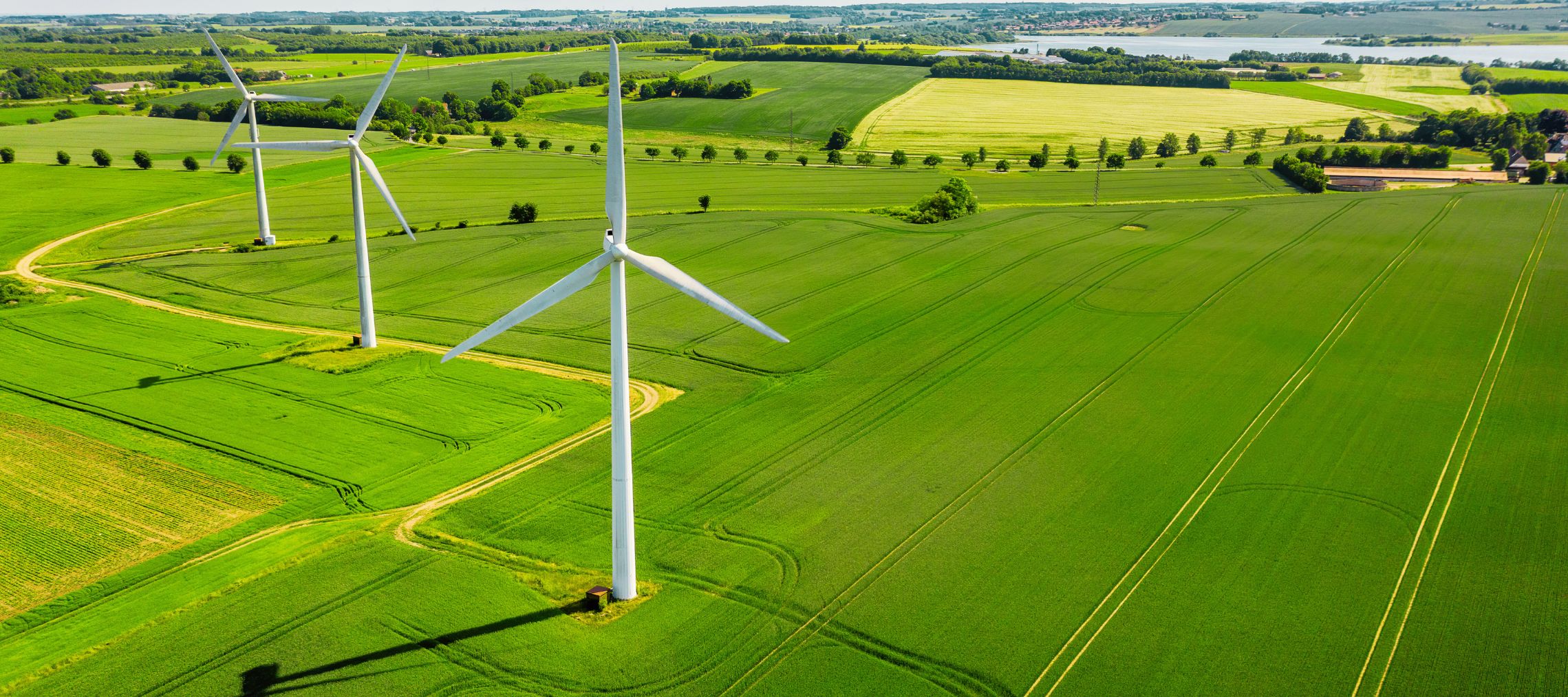





Distributed solar: The future of energy resilience in urban India
The urban population in India—the world’s most populous country—is expected to reach 675 million by 2035 as per the World Cities Report 2022 by UN-Habitat. As most commercial and industrial activities occur in urban areas and electricity is a major factor for development, this population increase will fuel a surge in electricity demand, leading to acute pressure on traditional energy grids and frequent blackouts.
Distributed solar financing: Unlocking investments for a greener future
The proliferation of distributed solar energy in India faces significant challenges, primarily due to the high initial investment costs of setting up a solar energy system. Also, the motivation to invest in these solutions is often found lacking, despite government subsidy schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyaan (PM-KUSUM) and the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana.
Unlocking the potential of Component A of PM-KUSUM
The 2019 Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) scheme aims to enhance energy security for farmers, while promoting the use of renewable energy (RE) in the agriculture sector. Of its three components, Component A focuses on the installation of decentralised grid-connected RE-based power plants, with capacities ranging from 500 kW to 2 MW, by farmers on their land. The component can provide an additional, stable stream of income to farmers through the provision of selling the excess electricity generated to the grid.
Budgeting for net zero: Government support needed to meet India’s clean energy goals
The Government of India has set ambitious goals to ramp up a range of clean technologies by 2030 to increase energy independence, security, and access while promoting industrial development and reducing air pollution and GHG emissions. To deliver on these goals, the government has introduced a suite of financial and non-financial support measures. But will these measures be sufficient to reach the goals in full and on time?
Mapping the resilience of renewable energy systems and assets in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan to extreme weather events
Climate hazards such as droughts, flood, and cyclones are becoming more severe and frequent, posing a threat to the resilience of renewable energy. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), India, in collaboration with the Center for Study of Science, Technology and Policy (CSTEP), conducted a study across four states in India (Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan) with a high percentage of wind and solar energy infrastructure. The study employed the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Assessment Report 5 (AR5) risk assessment framework.
Investment dynamics: Balancing opportunities and risks in India’s energy transition
India has witnessed remarkable growth in the solar sector over the last decade. According to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, the overall installed capacity has increased from 2.82 GW in March 2014 to 87.2 GW in July 2024.This can be attributed to aggressive government targets, supportive policy frameworks, decreasing technology costs, and increasing awareness about climate change. While the sector is attracting significant investments from foreign and domestic sources, it also has inherent risks.
Sustainable Homes: Potential of BIPV to reshape India’s urban architecture
India’s urban areas are expected to house about 600 million people by 2031 and 850 million people by 2051, as per the Handbook of Urban Statistics (2016) by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs. However, as per an estimate by the World Bank, about 70 per cent of the urban infrastructure needed by 2047 is yet to be built. Given this massive impending growth and infrastructure requirement, there is an urgent need for energy-efficient and sustainable building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) solutions.
How well is India tapping its rooftop solar potential?
Rooftop solar (RTS) has the potential to revolutionise India’s energy landscape, offering a sustainable, decentralised, and affordable solution to meet the country’s growing electricity needs and making consumers self-reliant. The country’s installed RTS capacity increased by 2.99 GW in 2023-2024, the highest growth reported in a year. As of March 31 this year, the total installed RTS capacity in India was 11.87 GW, per the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Decarbonising the MSME manufacturing sector in India
Small industries or micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are a crucial sector in India’s development. They have a large carbon footprint, partly because of the nature of energy consumption, with over 80% of the energy consumed being required for thermal processes to produce heat (e.g. in boilers and furnaces). These thermal energy demands have traditionally been met through fossil fuel sources (such as coal, natural gas, and pet coke), making MSMEs a hard-to-abate sector.
Press Release: Scope for deep decarbonisation in the MSME manufacturing sector
Bengaluru, 28 June 2024: The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) contribute to 31% of India’s gross domestic product, almost 50% of exports, and 57% of all employment in manufacturing sectors, making them crucial to the economy. However, they are highly energy- and emission-intensive.