As a developing economy, India has numerous developmental aspirations. How India meets these goals without worsening the climate crisis is at the heart of CSTEP's work. Addressing climate change and enabling a secure and sustainable future for Indian citizens require an overhaul of previous paradigms on development and resource utilisation. This is reflected in our work on developing low-carbon trajectories for development with an emphasis on nature-based solutions.
We are working with state governments across India to build capacity on risk and vulnerability assessments to inform their respective action plans on climate change. The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy is crucial to achieving a secure and sustainable future. CSTEP's studies explore the possibility of a greater integration of renewables in the energy sector.








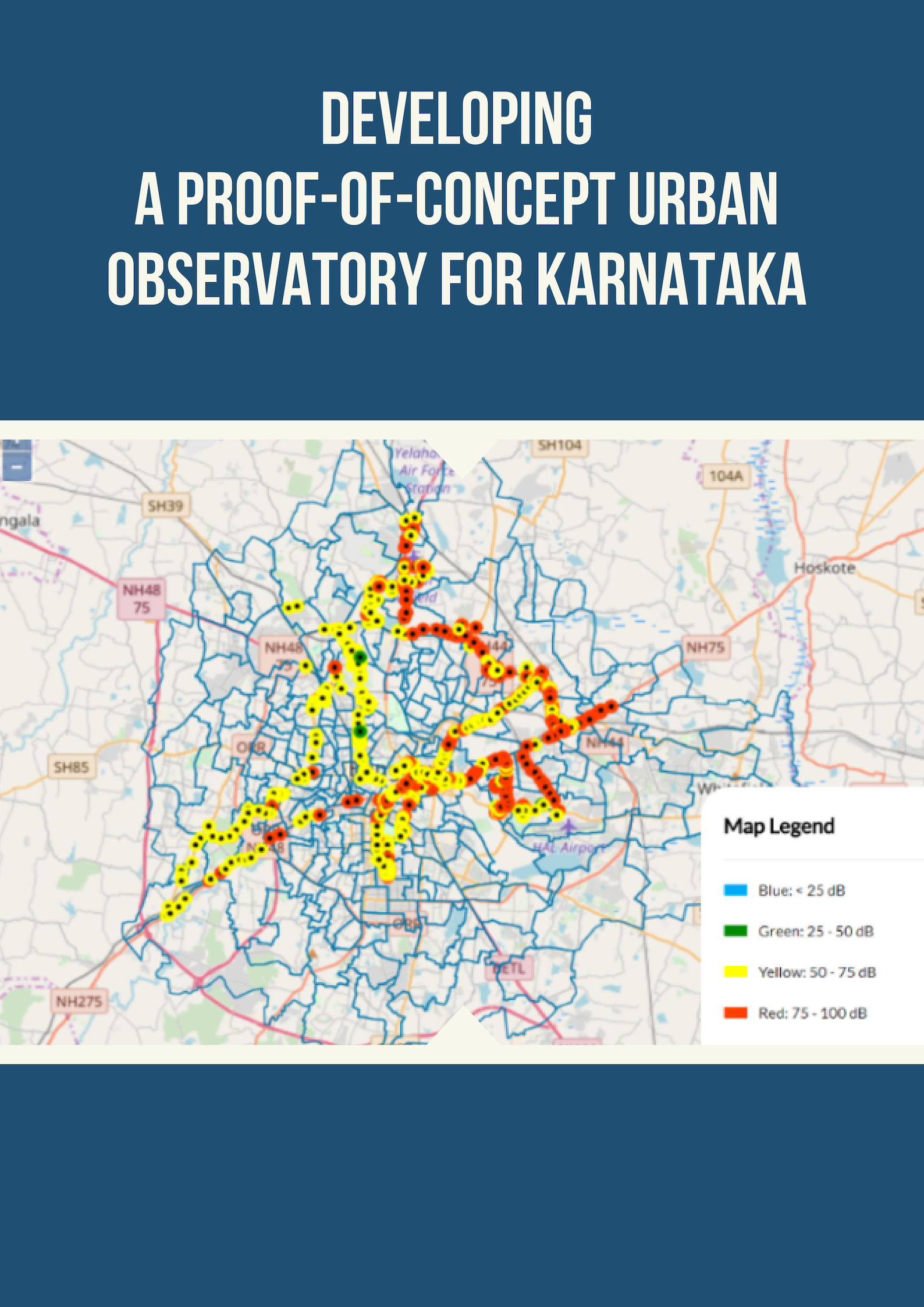








Namma SAFARI: Low-carbon development pathways for Karnataka
The need for climate action is well established, not only to mitigate climate change but also to build resilience and prevent the depletion of resources due to overexploitation. Creating a roadmap towards a sustainable future requires a deep understanding of how each sector is expected to grow, and more importantly, how different sectors would interact with each other to co-evolve dynamically. Several models at the global scale and a few at the Indian scale have been created to facilitate this understanding.
Whither our city?
The past week has been bleak in Bengaluru. What initially brought relief to the hot summers quickly turned into a nightmare. According to the India Meteorological Department (IMD), the city has already breached the 100 mm rainfall/day mark this month, classifying the event as ‘heavy rainfall’. The high-intensity rains over the past few days have disrupted lives, resulting in waterlogged roads, submerged underpasses, overflowing drains, fallen trees, and widespread power outages.
